전체 코드는 더보기 참고
더보기
void *
__libc_malloc (size_t bytes)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
void *victim;
void *(*hook) (size_t, const void *)
= atomic_forced_read (__malloc_hook);
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))
return (*hook)(bytes, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));
arena_get (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
/* Retry with another arena only if we were able to find a usable arena
before. */
if (!victim && ar_ptr != NULL)
{
LIBC_PROBE (memory_malloc_retry, 1, bytes);
ar_ptr = arena_get_retry (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
}
if (ar_ptr != NULL)
(void) mutex_unlock (&ar_ptr->mutex);
assert (!victim || chunk_is_mmapped (mem2chunk (victim)) ||
ar_ptr == arena_for_chunk (mem2chunk (victim)));
return victim;
}
libc_hidden_def (__libc_malloc)
변수 및 인자
void *
__libc_malloc (size_t bytes)
{
mstate ar_ptr;
void *victim;- bytes : 할당할 크기
- ar_ptr : 아레나 주소
- victim : 반환될 청크 주소
__malloc_hook
void *(*hook) (size_t, const void *)
= atomic_forced_read (__malloc_hook);
if (__builtin_expect (hook != NULL, 0))
return (*hook)(bytes, RETURN_ADDRESS (0));__malloc_hook에 저장된 값이 있으면 저장된 함수를 호출한다
상세과정은 아래 더보기
더보기
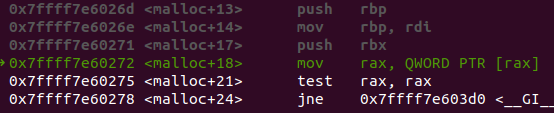
check __malloc_hook

__malloc_hook


atomic_forced_read 매크로 __malloc_hook의 값을 가져와 NULL이 아니면 해당 함수를 호출하게 된다
첫 malloc을 호출할 때 __malloc_hook이 호출된다??
void *weak_variable (*__malloc_hook)
(size_t __size, const void *)= malloc_hook_ini;실제 디버깅을 해보거나 malloc.c코드를 분석해보면 처음 malloc을 호출할때 __malloc_hook에 저장된 malloc_hook_ini함수를 호출한다
static void *
malloc_hook_ini (size_t sz, const void *caller){
__malloc_hook = NULL;
ptmalloc_init ();
return __libc_malloc (sz);
}malloc_hook_ini함수에서는 수행하는 동작은 아래와 같다
- __malloc_hook NULL로 초기화
- ptmalloc_init함수 호출
- malloc함수 재호출
arena_get 과 _int malloc
arena_get (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);arena_get함수에서는 ar_ptr에 현재 아레나를 저장하고 뮤텍스를 lock한다 (상세과정 아래 더보기)
더보기
/* arena_get() acquires an arena and locks the corresponding mutex.
First, try the one last locked successfully by this thread. (This
is the common case and handled with a macro for speed.) Then, loop
once over the circularly linked list of arenas. If no arena is
readily available, create a new one. In this latter case, `size'
is just a hint as to how much memory will be required immediately
in the new arena. */
#define arena_get(ptr, size) do { \
ptr = thread_arena; \
arena_lock (ptr, size); \
} while (0)위 주석에 설명한 내용을 토대로 동작을 보면 arena를 받아오고 뮤텍스를 잠근다
_int_malloc에서는 할당될 청크의 주소를 정해 반환하는 작업을 수행한다 (상세 과정은 아래 링크글 참고)
retry
/* Retry with another arena only if we were able to find a usable arena
before. */
if (!victim && ar_ptr != NULL)
{
LIBC_PROBE (memory_malloc_retry, 1, bytes);
ar_ptr = arena_get_retry (ar_ptr, bytes);
victim = _int_malloc (ar_ptr, bytes);
}만약 호출에 실패하면 한번 더 시도한다
check
if (ar_ptr != NULL)
(void) mutex_unlock (&ar_ptr->mutex);
assert (!victim || chunk_is_mmapped (mem2chunk (victim)) ||
ar_ptr == arena_for_chunk (mem2chunk (victim)));
return victim;이 후에 ar_ptr(아레나 포인터)에 저장된 아레나에 mutext_unlock함수를 호출하고 검사를 통과하면 victim을 반환 하게 된다
사용된 주요함수
reference
https://blog.naver.com/yjw_sz/221549666704
24. glibc 2.23 malloc.c 분석2 (libc_malloc, int_malloc)
libc_malloc과 int_malloc을 분석 해보고자 한다. malloc을 호출할 때 가장 먼저 실행되는건 libc_malloc이...
blog.naver.com
'Heap analysis > glibc 2.23' 카테고리의 다른 글
| (glibc 2.23) malloc_consolidate (0) | 2022.04.26 |
|---|---|
| (glibc 2.23) _int_malloc (0) | 2022.04.25 |
| (glibc 2.23) _int_free (0) | 2022.04.25 |
| (glibc 2.23) unlink (0) | 2022.04.22 |
| (glibc 2.23)check_malloced_chunk (0) | 2022.03.30 |


